AFVs are vehicles that are powered by a fuel other than conventional petrol or diesel. Examples of such are battery electric vehicles, plug-in hybrid vehicles and hydrogen-powered vehicles.
Examples: Teslas, BMW i3, Mini Electric, Toyota Prius, Toyota Mirai
EV Glossary
Welcome to our new EV glossary
Over the next few weeks, we will be adding many more terms, covering everything from vehicle and battery types to charging and autonomous driving.
AFV – Alternative Fuel Vehicle
AWD – All Wheel Drive
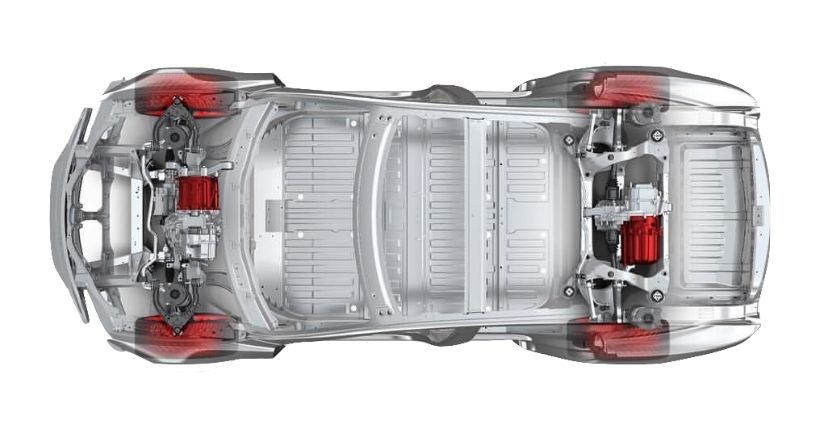
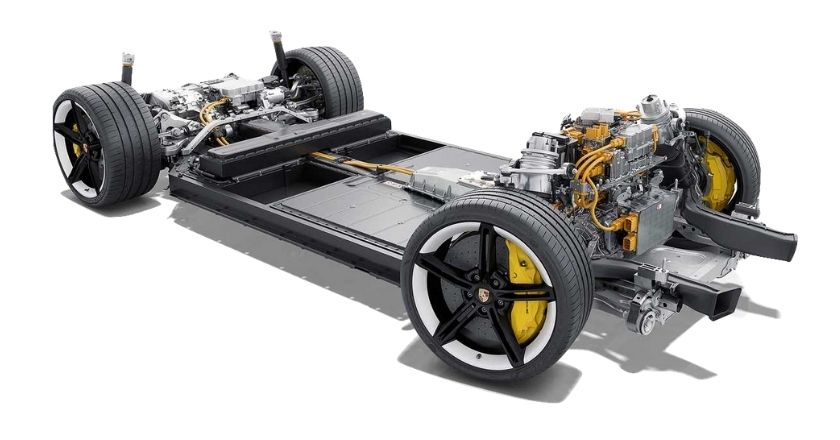
AWD stands for all-wheel-drive, which sends power to both the front and rear pairs of wheels. All-wheel-drive cars typically use their systems to maximise road-holding and traction by allowing each wheel to spin at a different speed. This is in contrast to four-wheel-drive vehicles that are geared for off-road ability. ICEV cars typically use a central differential to distribute torque between the front and rear axles. Conversely, modern EVs commonly use a dual-motor setup to drive the front and rear axles. Examples, include Tesla Model S Performance, Jaguar I-Pace, Audi e-Tron
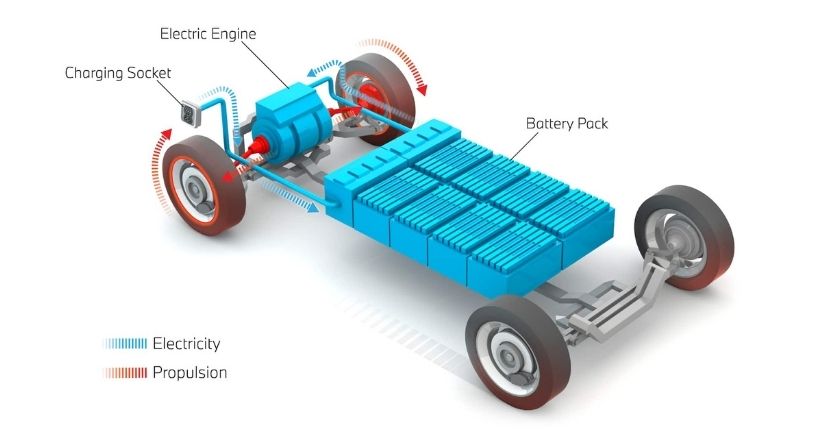
BEV – Battery Electric Vehicle
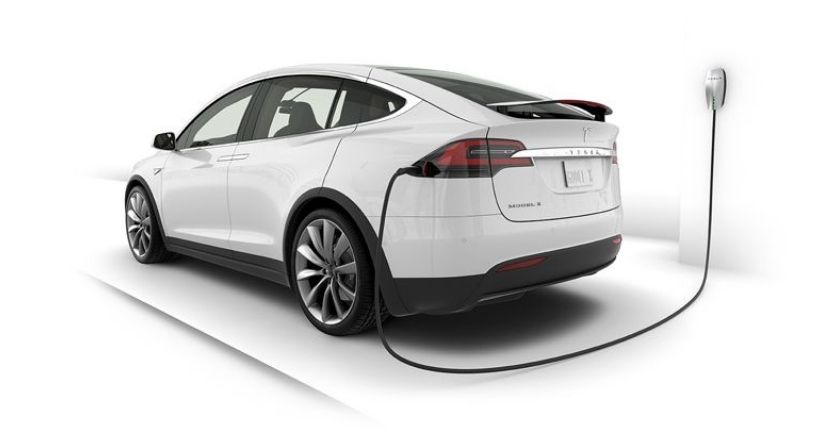
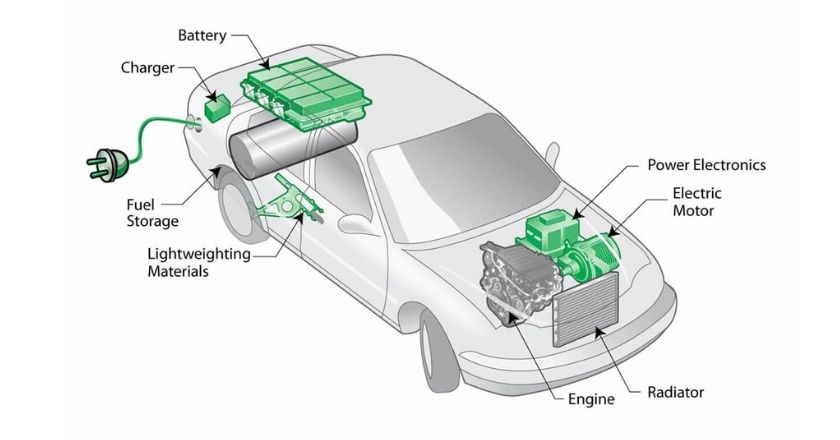
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) are vehicles that are powered solely by electricity stored within an on-board-battery. They are recharged by plugging the car into a mains outlet or a dedicated electric vehicle fast charger, and range is typically restricted by battery capacity. BEVs do not emit emissions.
Examples: Nissan Leaf, all Teslas, Hyundai Kona, Porsche Taycan
Electrified
Electrified is the term given to something that has been powered by or converted to run on electricity. In automotive terms, this could be used to describe an existing car within a manufacturers portfolio that has had an electric offering introduced. Eg: The Porsche Macan line-up will be electrified with the introduction of the Macan EV. It could also refer to a car that has been retrofitted with an electric motor, such as the Jaguar E-Type Zero.
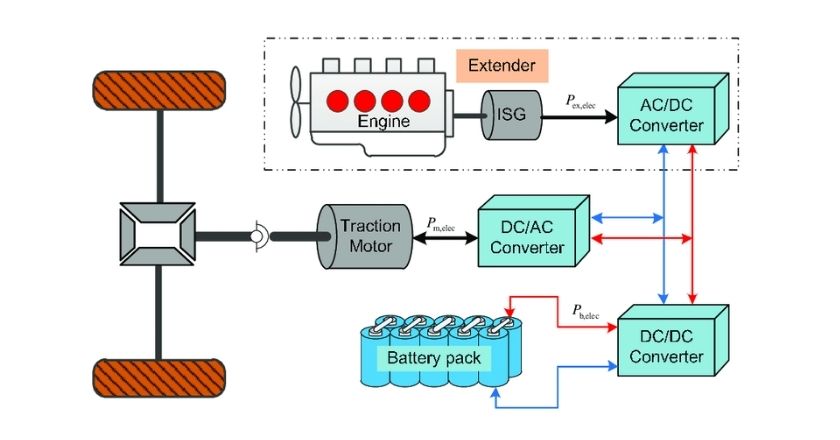
EREV – Extended-range electric vehicle (or REx)
An Electric-Range Extended Vehicle or Range Extender vehicle is the term given to a battery-powered vehicle that has a form of on-board charging capability — traditionally this comes in the form of a petrol or diesel generator. This differs from a Hybrid, as the fossil-fuel motor is not connected to the drive wheels, but rather only re-charges the battery.
Examples: Chevrolet Volt. BMW i3 REx
EV – Electric Vehicle
An EV is the broad acronym given to vehicles that are powered by electricity. While it can refer to vehicles that utilise electricity in part (such as PHEVs or EREVs), it is typically the term used to describe vehicles that are solely battery powered — otherwise known as BEVs (Battery Electric Vehicles).
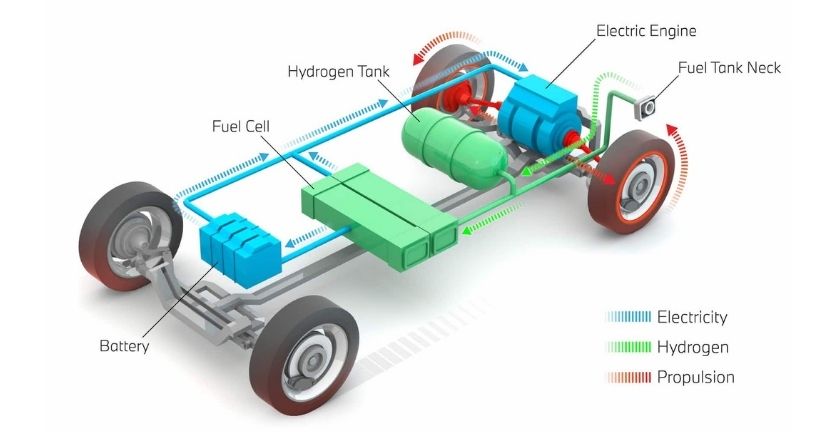
FCEV – Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle
A Fuel Cell Electric vehicle is a hydrogen-powered vehicle that converts hydrogen into electricity. Unlike combusting fuel in an internal combustion engine (like petrol or diesel), in an FCEV hydrogen is converted to electricity through an electrochemical reaction. The electricity then powers an electric motor, which provides motive force. The only emission of an FCEV is water.
Examples: Toyota Mirai, Hyundai Nexo, Hyundai iX35 FCEV
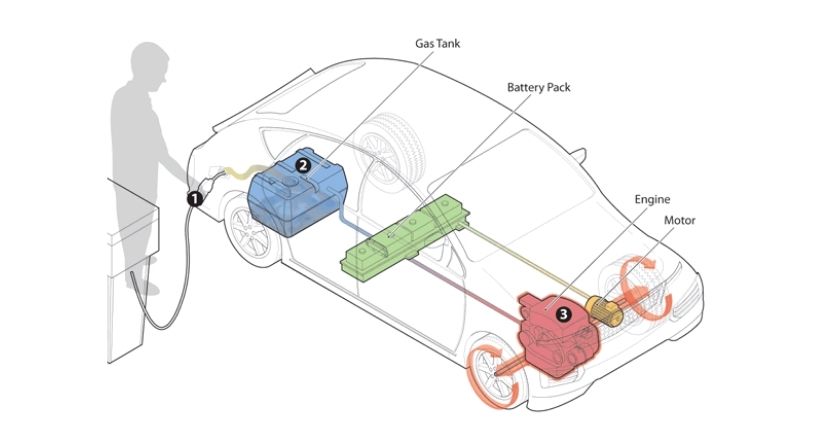
HEV – Hybrid Electric Vehicle
A HEV, otherwise known simply as a Hybrid, is a vehicle which is powered both by an internal combustion engine (either petrol or diesel) that is in tandem with an electric motor. Unlike PHEVs, HEV batteries cannot be recharged by a mains outlet or dedicated charger. Electricity is generated solely through the ICE (Internal Combustion Engine), which recharges the on-board batteries as well as driving the wheels. Electric-only range is typically limited, and such vehicles will always require fossil fuel to run.
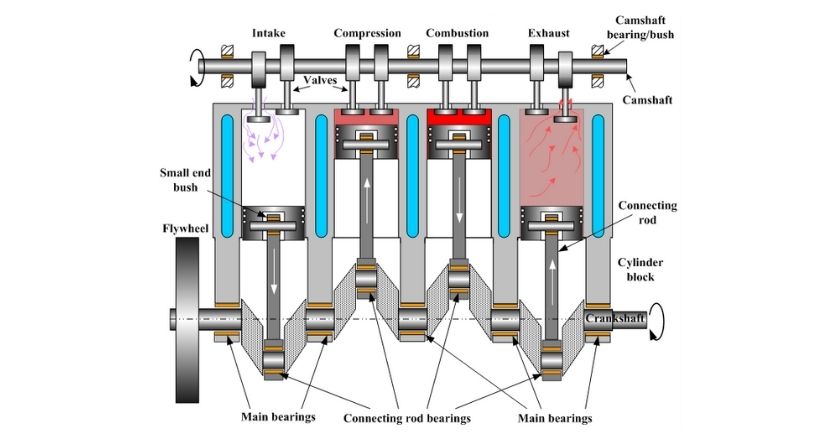
ICE – Internal Combustion Engine
An internal combustion engine is an engine that runs on fossil fuel — typically petrol, diesel or LPG. The Internal Combustion Engine is the most common form of engine in cars throughout the last century. Power is produced via a combustion cycle within the engine.
ICEV – Internal Combustion Engine Vehicle
An Internal Combustion Engine Vehicle is a vehicle that features an internal combustion engine that provides the sole source of power to the drive wheels.
Examples: Mercedes-Benz C63, Toyota Corolla, Suzuki Swift
PEV – Pure Electric Vehicles
A Pure Electric Vehicle is a vehicle, such as a Nissan Leaf or any Tesla, which runs solely on power stored within its onboard battery packs. Pure EVs have no way of extending their range once their batteries are depleted, and can only be recharged via a mains outlet or dedicated electric vehicle fast charger. See also BEVs